Design Science Research according to Kuechler & Vaishnavi: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "== Process description == thumb Design cycle according to Kuechler & Vaishnavi (2008) == Awareness of Problem == === Description === Describ...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
== Evaluation == | == Evaluation == | ||
=== Description === | === Description === | ||
[[File: | [[File:Evaluation.png|thumb]] | ||
Evaluate the artifact according to criteria that are made in the 'Awareness of Problem' activity. | Evaluate the artifact according to criteria that are made in the 'Awareness of Problem' activity. | ||
Revision as of 10:08, 22 March 2020
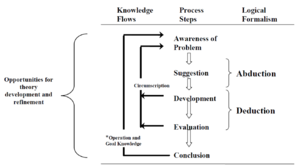
Process description
Design cycle according to Kuechler & Vaishnavi (2008)
Awareness of Problem
Description
Describe the awareness of an interesting problem. Awareness can come from new developments in the industry or from other reference disciplines.
Examples
Expert interviews with eight employees of the case company revealed:
- Lack of process (model) understanding Difficulties in execution business processes
- Structured literature review on the concept “guidance” in IS research
Structured literature review on the concept “guidance” in IS research:
- Overview on existing research
- Taxonomy of guidance in IS research
Further Readings
Kuechler, B., and Vaishnavi, V. 2008. On Theory Development in Design Science Research: Anatomy of a Research Project, European Journal of Information Systems (17:5), pp. 489-504.
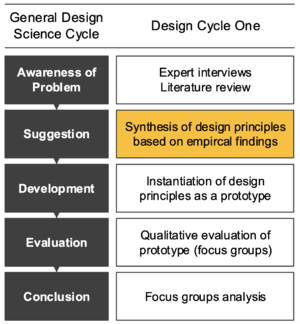
Suggestion
Description
Synthesis of design principles based on empirical findings: Extraction of Meta-Requirements from existing literature. Derivation of Design Principles based on the Meta- Requirements. Selection of Design Decisions to implement the Design Principles.
Examples
Further Readings
Kuechler, B., and Vaishnavi, V. 2008. On Theory Development in Design Science Research: Anatomy of a Research Project, European Journal of Information Systems (17:5), pp. 489-504.
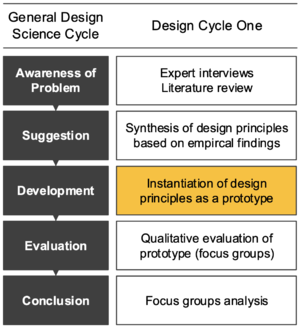
Development
Description
Implement the suggested design. Different techniques can be used depending on the artifact to be constructed.
Examples
Instantiation of design principles as a prototype
Further Readings
Kuechler, B., and Vaishnavi, V. 2008. On Theory Development in Design Science Research: Anatomy of a Research Project, European Journal of Information Systems (17:5), pp. 489-504.
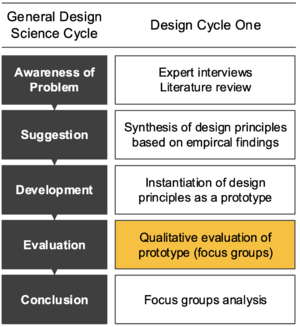
Evaluation
Description
Evaluate the artifact according to criteria that are made in the 'Awareness of Problem' activity.
Examples
Qualitative evaluation of the prototype by eg. focus group workshops in the case company:
- SWOT analysis
- Feedback by the participants
Further Readings
Kuechler, B., and Vaishnavi, V. 2008. On Theory Development in Design Science Research: Anatomy of a Research Project, European Journal of Information Systems (17:5), pp. 489-504.
Conclusion
Description
Write up the results and explain the gained knowledge. Learnings can be described as 'firm' facts that can be:
- repeatably applied
- repeatably invoked
Or there are findings that may serve as the subject of further research.
Examples
Further Readings
Kuechler, B., and Vaishnavi, V. 2008. On Theory Development in Design Science Research: Anatomy of a Research Project, European Journal of Information Systems (17:5), pp. 489-504.