Action Design Research according to Sein et al: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Problem Formulation == | == Problem Formulation == | ||
=== Description === | === Description === | ||
Tasks to be performed in the problem formulation activity: | Tasks to be performed in the problem formulation activity: | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
=== Further Readings === | === Further Readings === | ||
Sein, Maung K.; Henfridsson, Ola; Purao, Sandeep; Rossi, Matti; and Lindgren, Rikard. 2011. "Action Design Research," MIS Quarterly, (35: 1) pp.37-56. | Sein, Maung K.; Henfridsson, Ola; Purao, Sandeep; Rossi, Matti; and Lindgren, Rikard. 2011. "Action Design Research," MIS Quarterly, (35: 1) pp.37-56. | ||
== Building, Intervention, and Evaluation == | == Building, Intervention, and Evaluation == | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 28 March 2020
Process description
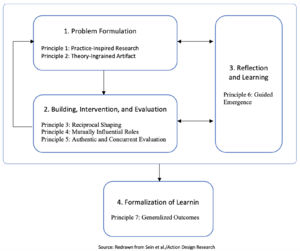
ADR is a research method for generating prescriptive design knowledge through building and evaluating ensemble IT artifacts in an organizational setting. It deals with two seemingly disparate challenges: (1) addressing a problem situation encountered in a specific organizational setting by intervening and evaluating; and (2) constructing and evaluating an IT artifact that addresses the class of problems typified by the encountered situation. The responses demanded by these two challenges result in a method that focuses on the building, intervention, and evaluation of an artifact that reflects not only the theoretical precursors and intent of the researchers but also the influence of users and ongoing use in context.
Problem Formulation
Description
Tasks to be performed in the problem formulation activity:
- Identify and conceptualize the research opportunity
- Formulate initial research questions
- Cast the problem as an instance of a class of problems
- Identify contributing theoretical bases and prior technology advances
- Secure long-term organizational commitment
- Set up roles and responsibilities
Examples
Further Readings
Sein, Maung K.; Henfridsson, Ola; Purao, Sandeep; Rossi, Matti; and Lindgren, Rikard. 2011. "Action Design Research," MIS Quarterly, (35: 1) pp.37-56.
Building, Intervention, and Evaluation
Description
Tasks to be performed in the building, intervention, and evaluation activity:
- Discover initial knowledge-creation target
- Select or customize BIE form
- Execute BIE cycle(s)
- Assess need for additional cycles, repeat
Examples
Provide some examples for the activity 2.
Further Readings
Sein, Maung K.; Henfridsson, Ola; Purao, Sandeep; Rossi, Matti; and Lindgren, Rikard. 2011. "Action Design Research," MIS Quarterly, (35: 1) pp.37-56.
Reflection and Learning
Description
Tasks in the reflection and learning activity:
- Reflect on the design and redesign during the project
- Evaluate adherence to principles
- Analyze intervention results according to stated goals
Examples
Further Readings
Sein, Maung K.; Henfridsson, Ola; Purao, Sandeep; Rossi, Matti; and Lindgren, Rikard. 2011. "Action Design Research," MIS Quarterly, (35: 1) pp.37-56.
Formalization of Learning
Description
- Tasks to be performed in the formulation of learning activity:
- Abstract the learning into concepts for a class of field problems
- Share outcomes and assessment with practitioners
- Articulate outcomes as design principles
- Articulate learning in light of theories selected
- Formalize results for dissemination
Examples
Further Readings
Sein, Maung K.; Henfridsson, Ola; Purao, Sandeep; Rossi, Matti; and Lindgren, Rikard. 2011. "Action Design Research," MIS Quarterly, (35: 1) pp.37-56.