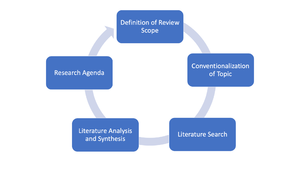
Literature Review according to vom Brocke et al
Process description
The literature review process is essential in any kind of research and its importance has never been in doubt. A literature review seeks to uncover the sources relevant to a topic under study and, thus, makes a vital contribution to the relevance and rigor of research. With the rapidly increasing number of potentially relevant publications, its difficulty is increasing as well. The following process proposed by vom Brocke et al.[1]
supports researchers in crafting an effective literature review and guidance on how to deal with the increasingly dynamic context of information systems (IS) research.
Definition of Review Scope
Description
In order to clearly define the scope of a review, the established taxonomy for literature reviews presented by Cooper[2] is used. Cooper’s taxonomy is comprised of six constituent characteristics:
- Focus: Most literature reviews focus on research outcomes, research methods, theories, and/or applications.
- Goal: Common goals of literature reviews include summarising, criticizing, and/or integrating findings.
- Organization: For organizing a literature review, Cooper suggests a historical, conceptual, or methodological structure.
- Perspective: Reflects whether a certain position is espoused or not.
- Audience: Particularly determines the writing style of the author(s).
- Coverage: Four levels of coverage can be distinguished
- Exhaustive: including the entirety of literature on a topic or at least most of it.
- Exhaustive with selective citation: Considering all the relevant sources, but describing only a sample.
- Representative: Including only a sample that typifies larger groups of articles.
- Central: Reviewing the literature pivotal to a topic.
Examples
Further Readings
Brocke, Jan vom; Simons, Alexander; Niehaves, Bjoern; Niehaves, Bjorn; Reimer, Kai; Plattfaut, Ralf; and Cleven, Anne, "RECONSTRUCTING THE GIANT: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF RIGOUR IN DOCUMENTING THE LITERATURE SEARCH PROCESS" (2009). ECIS 2009 Proceedings. 161. http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2009/161
Cooper, H.M. (1988). Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society, 1, 104-126.
Conceptualization of Topic
Description
In this activity, attention should be paid to the fact that a review must begin with “a broad conception of what is known about the topic and potential areas where knowledge may be needed”[3]. Therefore, working definitions of the key terms should be provided at this point. This can be achieved by consulting “those sources most likely to contain a summary or overview of the key issues relevant to a subject,”[4] such as seminal textbooks, encyclopedias, or handbooks. A reasonable way of identifying key concepts is represented by concept mapping, which also provides the opportunity to uncover relevant search terms that can be applied in the subsequent literature search.
Examples
Introducing working definitions of terms, e.g. ‘literature review’
Further Readings
Brocke, Jan vom; Simons, Alexander; Niehaves, Bjoern; Niehaves, Bjorn; Reimer, Kai; Plattfaut, Ralf; and Cleven, Anne, "RECONSTRUCTING THE GIANT: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF RIGOUR IN DOCUMENTING THE LITERATURE SEARCH PROCESS" (2009). ECIS 2009 Proceedings. 161. http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2009/161
Literature Search
Description
Describe the Activity X.
Examples
Further Readings
Brocke, Jan vom; Simons, Alexander; Niehaves, Bjoern; Niehaves, Bjorn; Reimer, Kai; Plattfaut, Ralf; and Cleven, Anne, "RECONSTRUCTING THE GIANT: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF RIGOUR IN DOCUMENTING THE LITERATURE SEARCH PROCESS" (2009). ECIS 2009 Proceedings. 161. http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2009/161
Literature Analysis and Synthesis
Description
Describe the Activity X.
Examples
Further Readings
Brocke, Jan vom; Simons, Alexander; Niehaves, Bjoern; Niehaves, Bjorn; Reimer, Kai; Plattfaut, Ralf; and Cleven, Anne, "RECONSTRUCTING THE GIANT: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF RIGOUR IN DOCUMENTING THE LITERATURE SEARCH PROCESS" (2009). ECIS 2009 Proceedings. 161. http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2009/161
Research Agenda
Description
Describe the Activity X.
Examples
Further Readings
Brocke, Jan vom; Simons, Alexander; Niehaves, Bjoern; Niehaves, Bjorn; Reimer, Kai; Plattfaut, Ralf; and Cleven, Anne, "RECONSTRUCTING THE GIANT: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF RIGOUR IN DOCUMENTING THE LITERATURE SEARCH PROCESS" (2009). ECIS 2009 Proceedings. 161. http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2009/161
References
- ↑ Brocke, Jan vom; Simons, Alexander; Niehaves, Bjoern; Niehaves, Bjorn; Reimer, Kai; Plattfaut, Ralf; and Cleven, Anne, "RECONSTRUCTING THE GIANT: ON THE IMPORTANCE OF RIGOUR IN DOCUMENTING THE LITERATURE SEARCH PROCESS" (2009). ECIS 2009 Proceedings. 161. http://aisel.aisnet.org/ecis2009/161
- ↑ Cooper, H.M. (1988). Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society, 1, 104-126.
- ↑ Torraco, R.J. (2005). Writing integrative literature reviews: Guidelines and examples. Human Resource Development Review, 4 (3), 356-367.
- ↑ Baker, M.J. (2000). Writing a Literature Review. Marketing Review, 1 (2), 219-247.